Ինչպես կատարել ֆյուչերսների առևտուր OKX-ում

What are Perpetual Futures Contracts?
A futures contract is an agreement between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price and date in the future. These assets can range from commodities such as gold or oil, to financial instruments like cryptocurrencies or stocks. This type of contract serves as a powerful tool to both protect against potential losses and to secure profits.
Perpetual futures contracts are a type of derivative that allows traders to speculate on the future price of an underlying asset without actually owning it. Unlike regular futures contracts that have a set expiration date, perpetual futures contracts do not expire. This means that traders can hold their positions for as long as they want, allowing them to take advantage of long-term market trends and potentially earn significant profits. Additionally, perpetual futures contracts often have unique features like funding rates, which help keep their price in line with the underlying asset.
Perpetual futures do not have settlement periods. You can hold a trade for as long as you want, as long as you have enough margin to keep it open. For example, if you buy BTC/USDT perpetual at $30,000, you will not be bound by any contract expiry time. You can close the trade and secure your profit (or take the loss) when you want. Trading in perpetual futures is not allowed in the U.S. But the market for perpetual futures is sizable. Almost 75% of cryptocurrency trading worldwide last year was in perpetual futures.
Overall, perpetual futures contracts can be a useful tool for traders looking to gain exposure to the cryptocurrency markets, but they also come with significant risks and should be used with caution.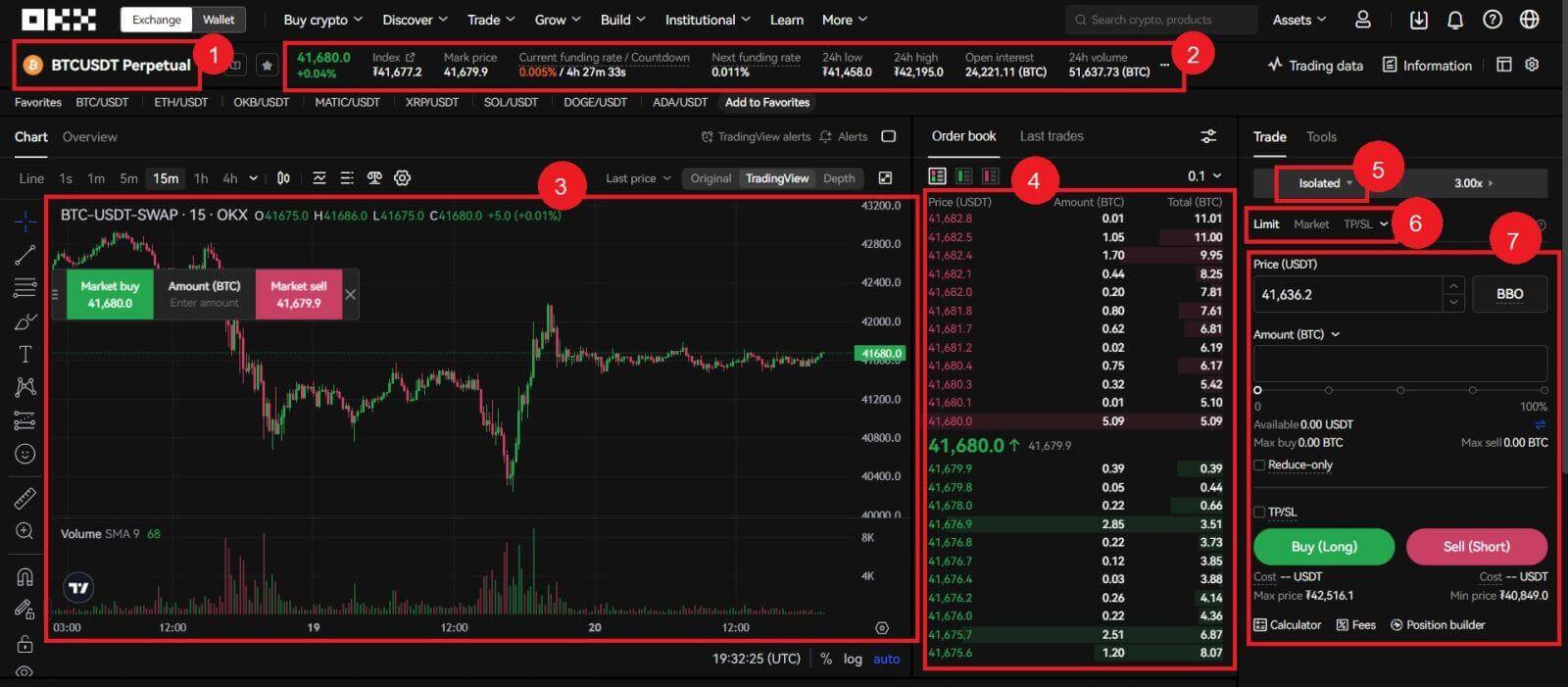 Futures trading interface:
Futures trading interface:
1. Trading Pairs: Shows the current contract underlying cryptos. Users can click here to switch to other varieties.
2. Trading Data and Funding Rate:Current price, highest price, lowest price, increase/decrease rate, and trading volume information within 24 hours. Display the current and next funding rate.
3. TradingView Price Trend: K-line chart of the price change of the current trading pair. On the left side, users can click to select drawing tools and indicators for technical analysis.
4. Orderbook and Transaction Data: Display current order book order book and real-time transaction order information.
5. Position and Leverage: Switching of position mode and leverage multiplier.
6. Order type: Users can choose from a limit order, market order and trigger order.
7. Operation panel: Allow users to make fund transfers and place orders.
How to Trade USDT-M Perpetual Futures on OKX (Web)
1. To trade on OKX, your funding account needs to be funded. Login to OKX and click on [Transfer] from the [Assets] dropdown list in the top menu. 2. Move coins or tokens from your “Funding” account to your “Trading” account to start trading. Once you’ve selected a coin or token and entered your desired amount to transfer, click [Transfer].
2. Move coins or tokens from your “Funding” account to your “Trading” account to start trading. Once you’ve selected a coin or token and entered your desired amount to transfer, click [Transfer].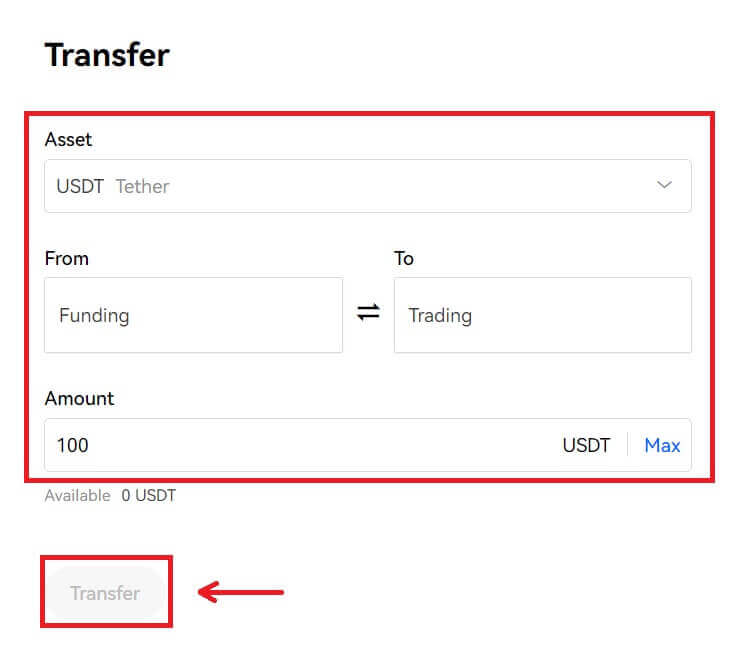
3. Navigate to [Trade] - [Futures]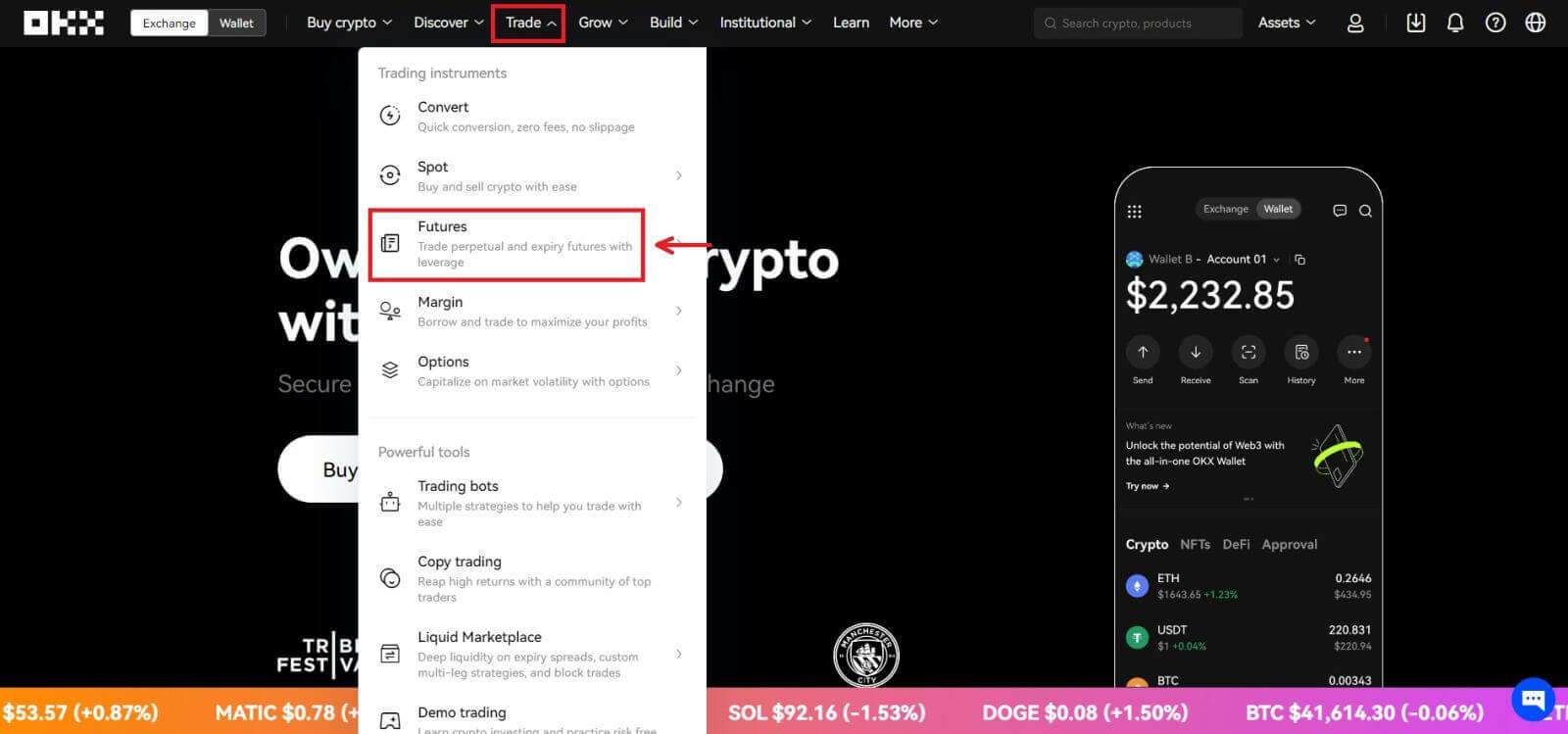 4. For this tutorial, we’ll select the [USDT-margined] - [BTCUSDT]. In this perpetual futures contract, USDT is the settlement currency, and BTC is the price unit of the futures contract.
4. For this tutorial, we’ll select the [USDT-margined] - [BTCUSDT]. In this perpetual futures contract, USDT is the settlement currency, and BTC is the price unit of the futures contract.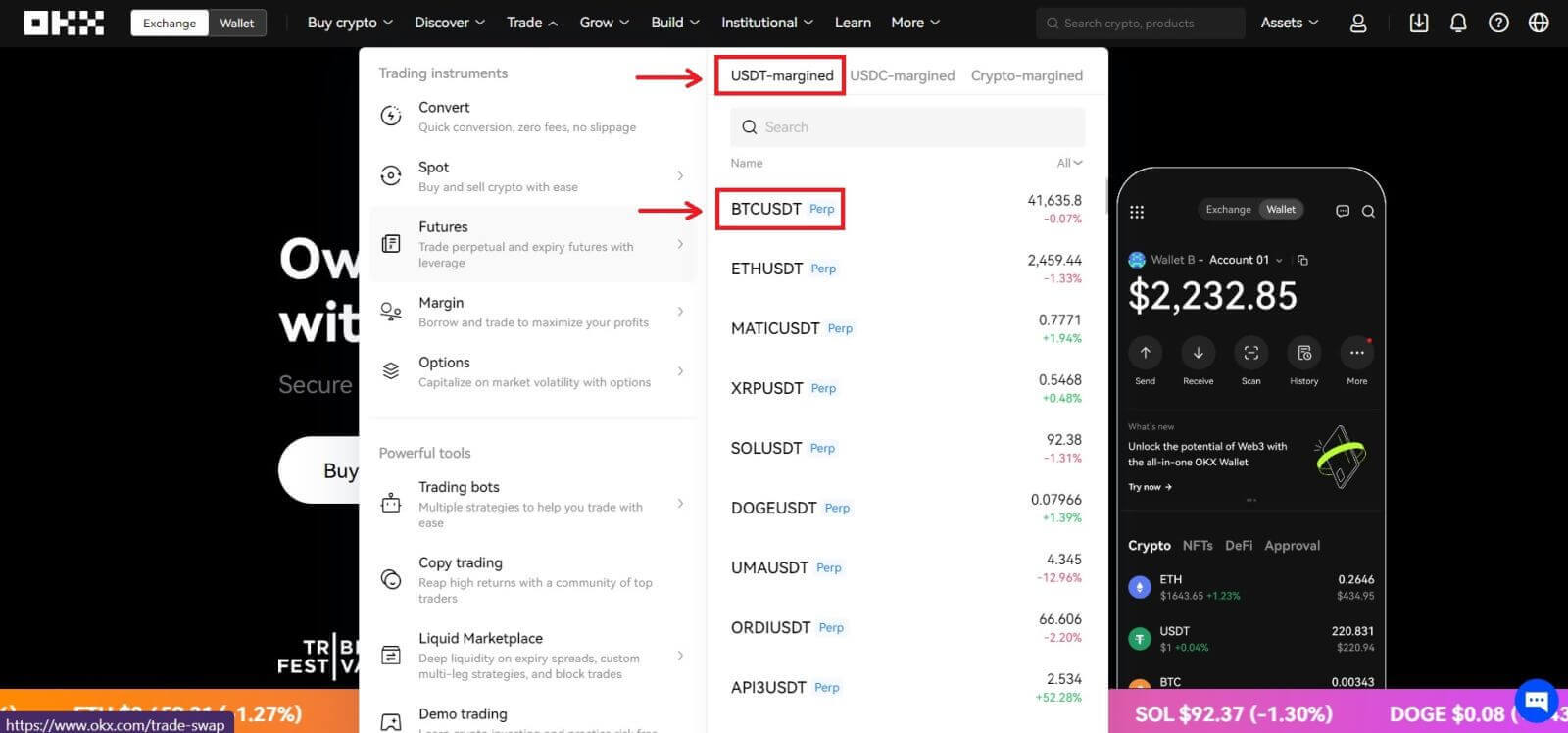 5. You can select the margin mode - Cross and Isolated.
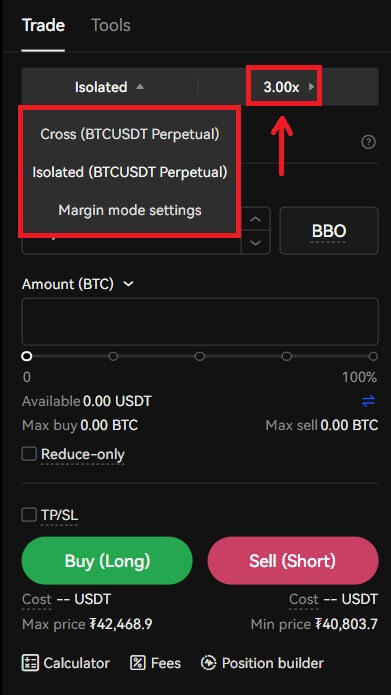
5. You can select the margin mode - Cross and Isolated.
- Cross margin utilizes all the funds in your futures account as the margin, including any unrealized profits from other open positions.
- Isolated on the other hand will only use an initial amount specified by you as the margin.
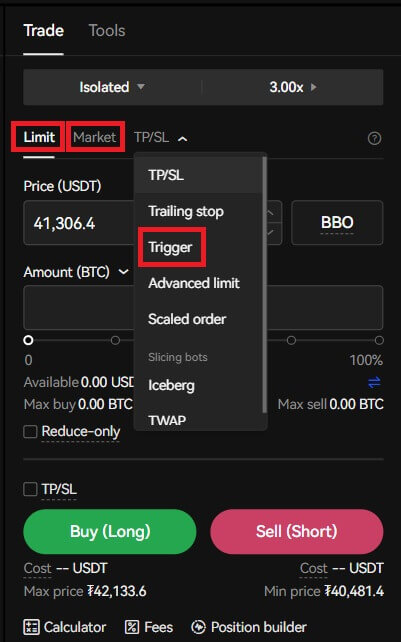
6. To open a position, users can choose between three options: Limit Order, Market Order, and Trigger Order.
- Limit Order: Users set the buying or selling price by themselves. The order will only be executed when the market price reaches the set price. If the market price does not reach the set price, the limit order will continue to wait for the transaction in the order book;
- Market Order: Market order refers to the transaction without setting the buying price or selling price. The system will complete the transaction according to the latest market price when placing the order, and the user only needs to enter the amount of the order to be placed.
- Trigger Order: Users are required to set a trigger price, order price and amount. Only when the latest market price reaches the trigger price, the order will be placed as a limit order with the price and amount set before.
7. Before you buy or sell, you can also select either Take profit or Stop loss. When using these options, you can enter conditions for taking profit and stopping loss.
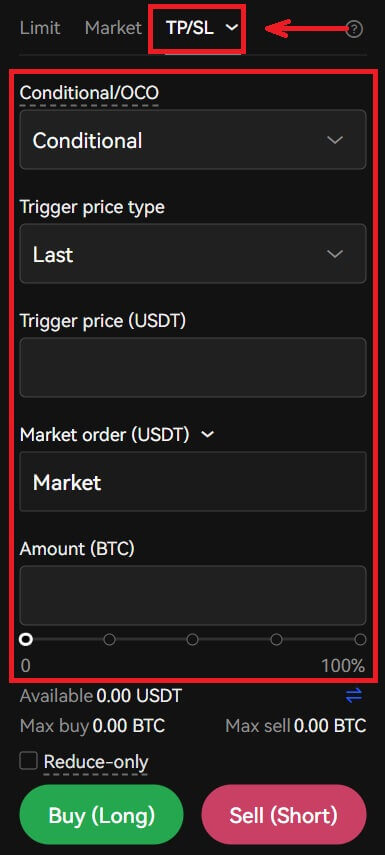
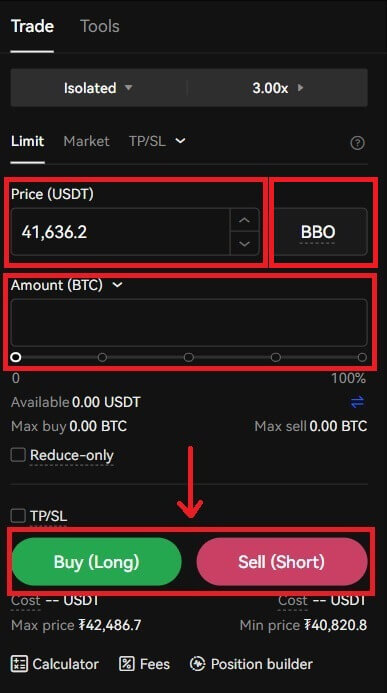
8. After selecting the margin type and leverage multiplier, you can choose the desired “Price” and “Amount” for the trade. If you would like to execute your order as soon as possible, you can click on BBO (i.e., the best bid offer).
After entering order details, you can click on [Buy (Long)] to enter a long contract (i.e., to buy BTC) or click on [Sell (Short)] if you would like to open a short position (i.e., to sell BTC).
- Buying long means that you believe the value of the asset that you are buying is going to rise over time, and you will profit from this rise with your leverage acting as a multiple on this profit. Conversely, you will lose money if the asset falls in value, again multiplied by the leverage.
- Selling short is the opposite, you believe that the value of this asset will fall over time. You will profit when the value falls, and lose money when the value increases.
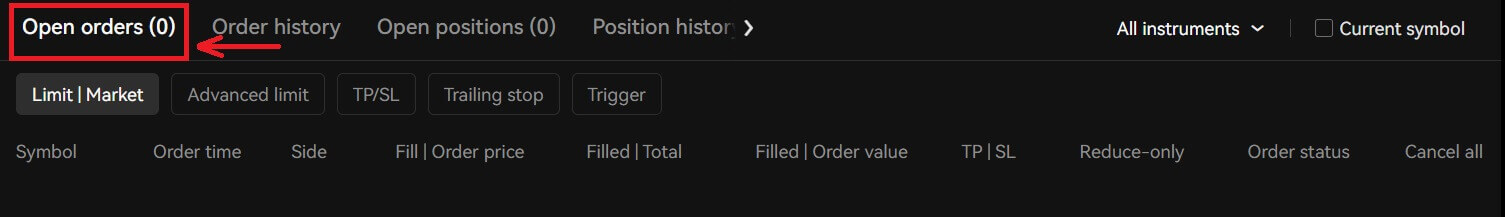
9. After placing your order, view it under "Open Orders" at the bottom of the page.
How to Trade USDT-M Perpetual Futures on OKX (App)
1. To trade on OKX, your funding account needs to be funded. Login to OKX and click on [Assets] - [Transfer].
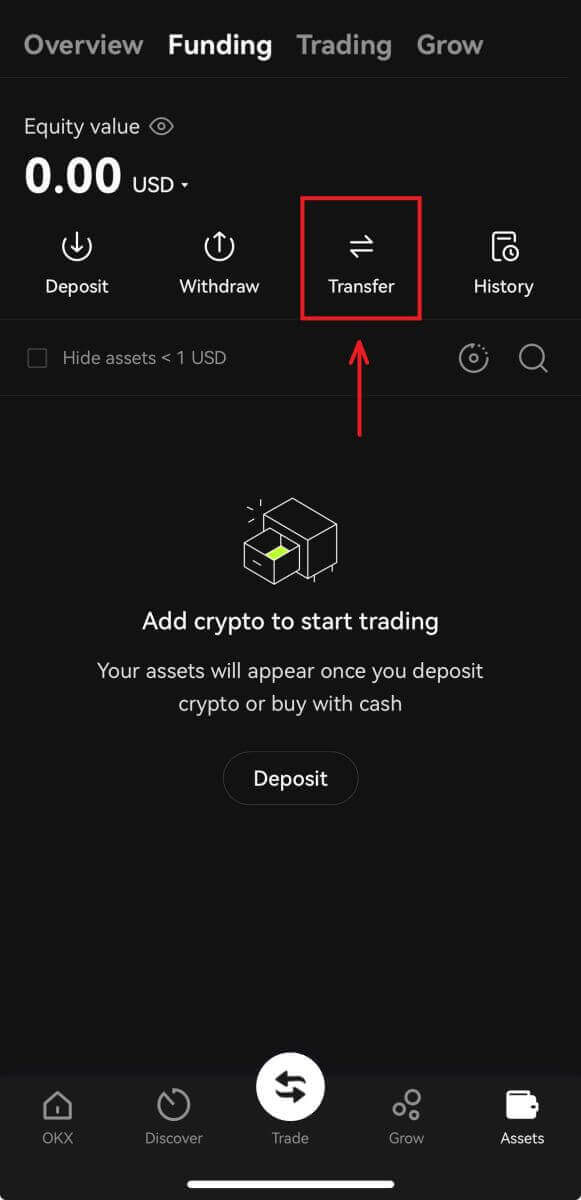
2. Move coins or tokens from your “Funding” account to your “Trading” account to start trading. Once you’ve selected a coin or token and entered your desired amount to transfer, click [Confirm].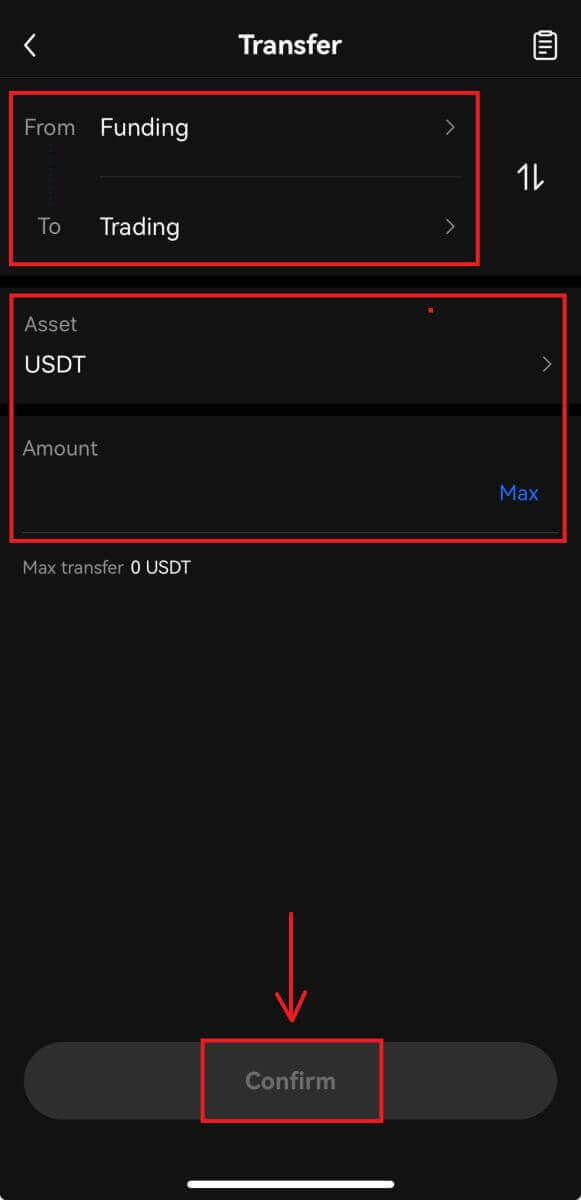
3. Navigate to [Trade] - [Futures].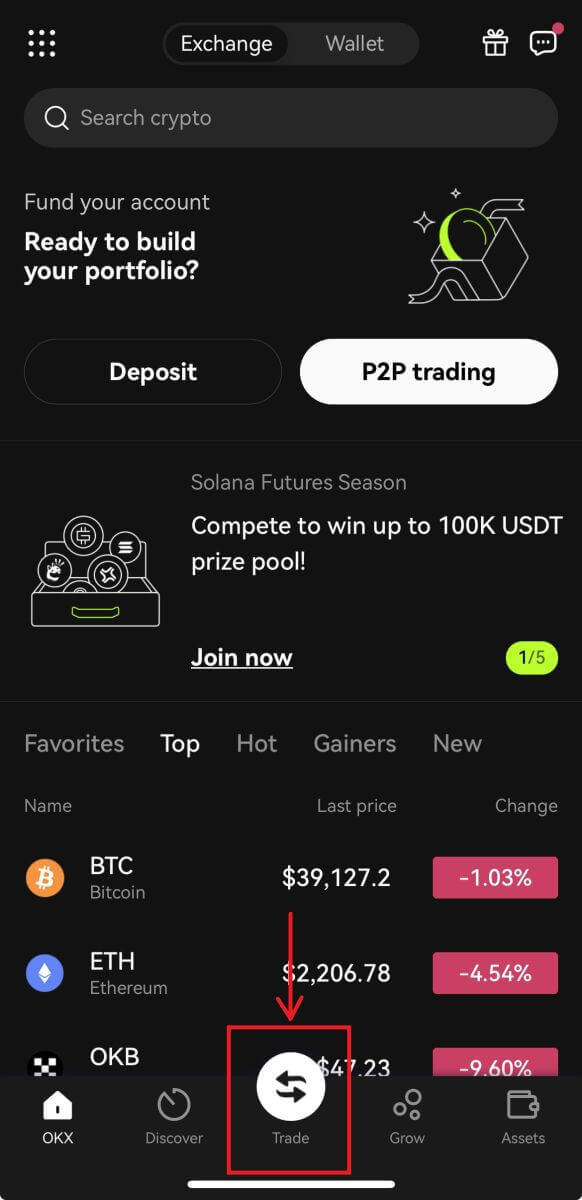
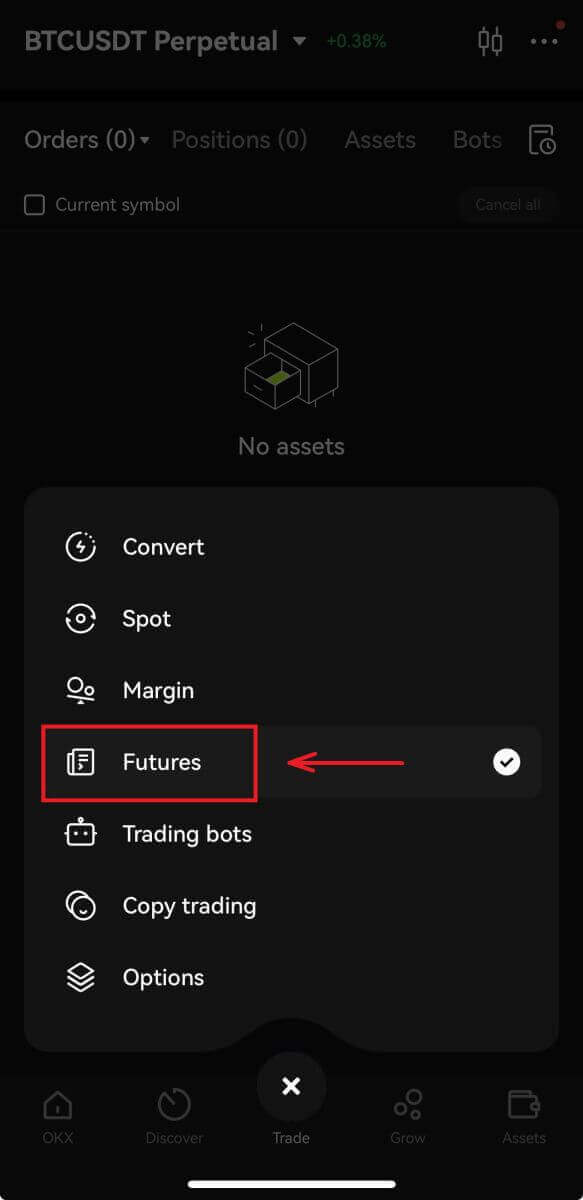
4. For this tutorial, we’ll select the [USDT-margined] - [BTCUSDT]. In this perpetual futures contract, USDT is the settlement currency, and BTC is the price unit of the futures contract.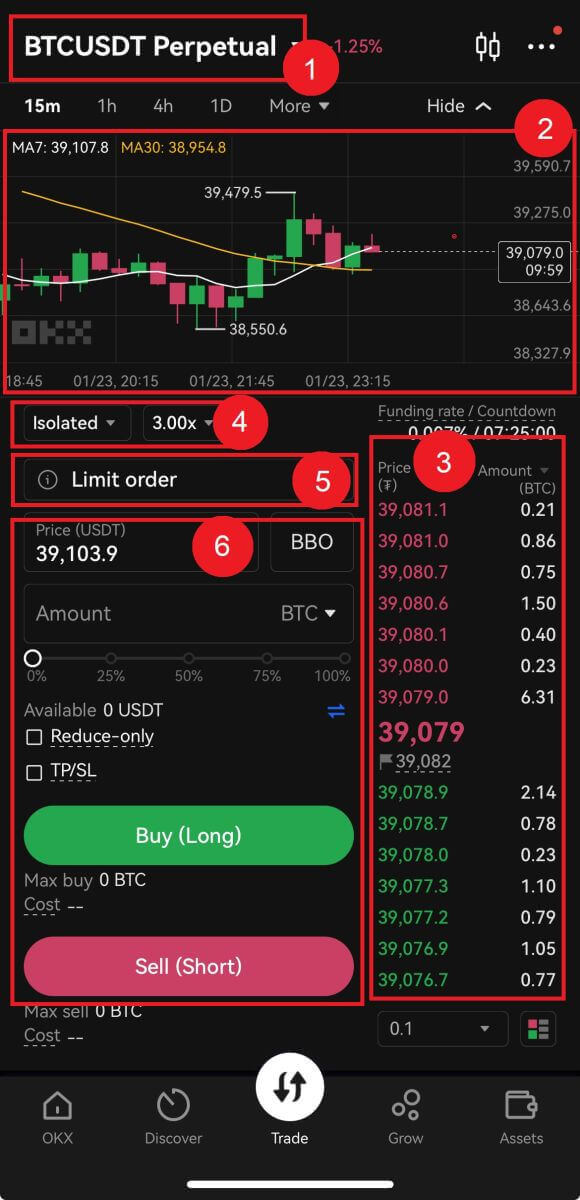
Futures trading interface:
1. Trading Pairs: Shows the current contract underlying cryptos. Users can click here to switch to other varieties.
2. TradingView Price Trend: K-line chart of the price change of the current trading pair. On the left side, users can click to select drawing tools and indicators for technical analysis.
3. Orderbook and Transaction Data: Display current order book order book and real-time transaction order information.
4. Position and Leverage: Switching of position mode and leverage multiplier.
5. Order type: Users can choose from a limit order, market order and trigger order.
6. Operation panel: Allow users to make fund transfers and place orders.
5. You can select the margin mode - Cross and Isolated.
- Cross margin utilizes all the funds in your futures account as the margin, including any unrealized profits from other open positions.
- Isolated on the other hand will only use an initial amount specified by you as the margin.
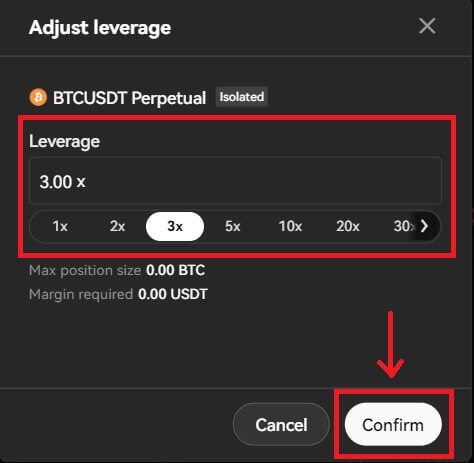
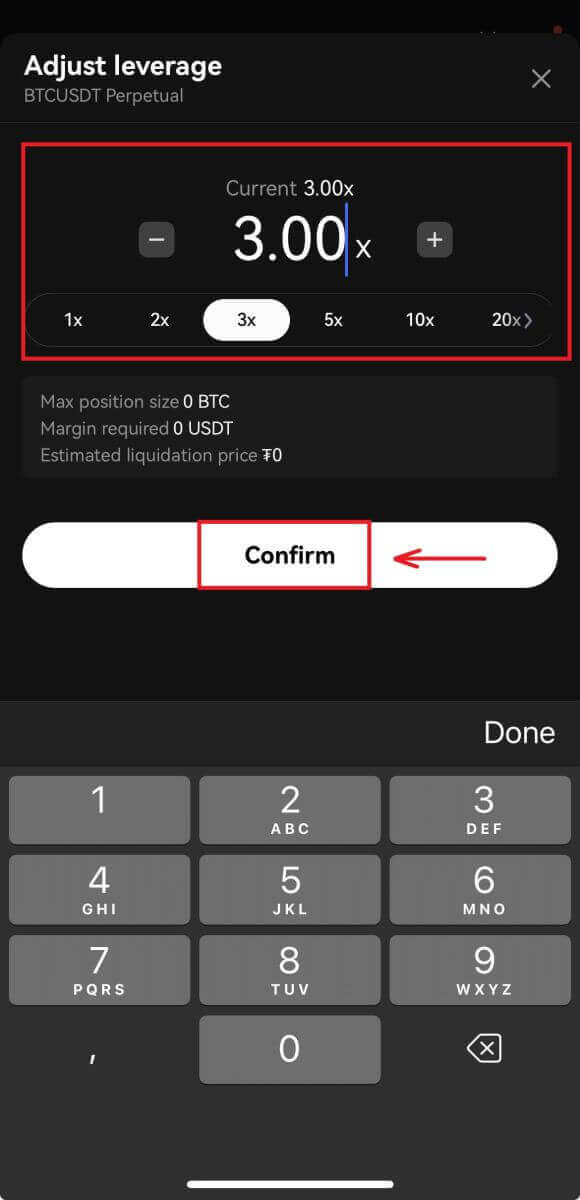
Adjust the leverage multiplier by clicking on the number. Different products support varying leverage multiples
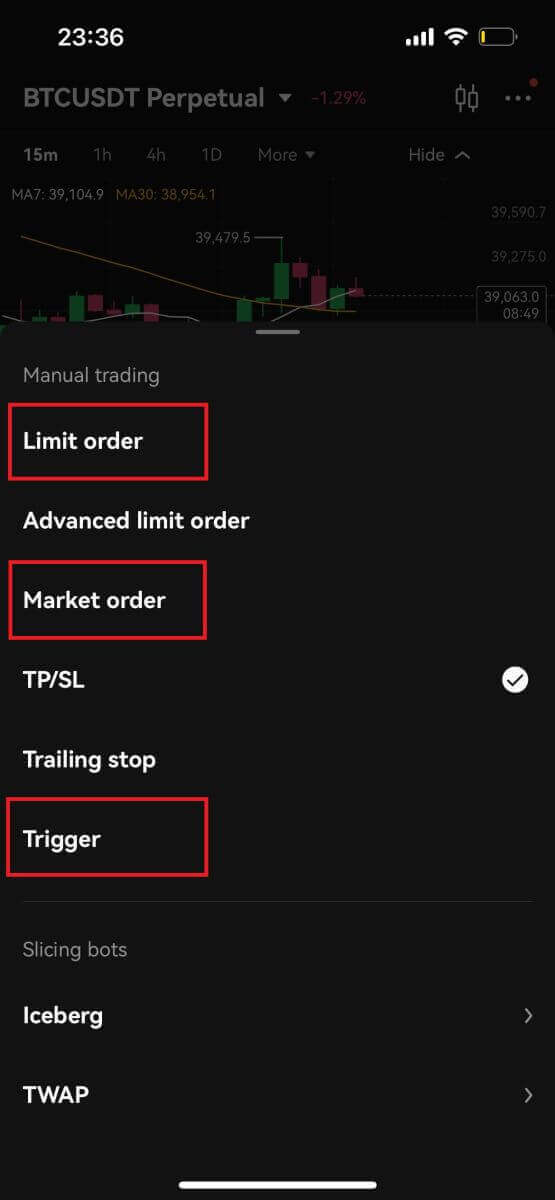
6. To open a position, users can choose between three options: Limit Order, Market Order, and Trigger Order. Enter the order price and quantity and click Open.
- Limit Order: Users set the buying or selling price by themselves. The order will only be executed when the market price reaches the set price. If the market price does not reach the set price, the limit order will continue to wait for the transaction in the order book;
- Market Order: Market order refers to the transaction without setting the buying price or selling price. The system will complete the transaction according to the latest market price when placing the order, and the user only needs to enter the amount of the order to be placed.
- Trigger Order: Users are required to set a trigger price, order price and amount. Only when the latest market price reaches the trigger price, the order will be placed as a limit order with the price and amount set before.
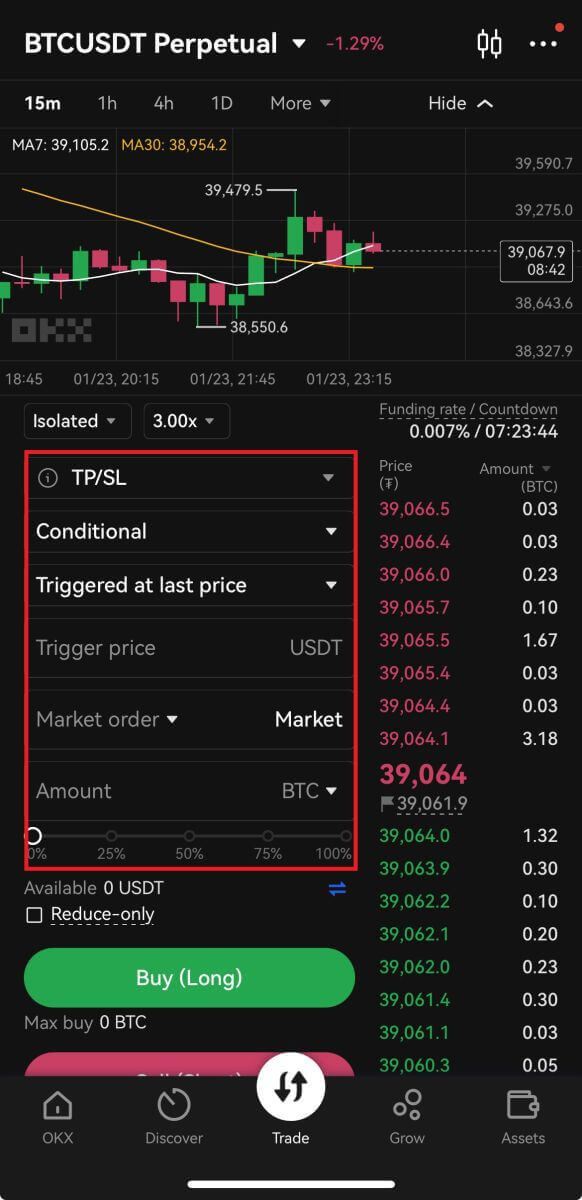
7. You can also select either Take profit or Stop loss. When using these options, you can enter conditions for taking profit and stopping loss.
8.After selecting the margin type and leverage multiplier, you can choose the desired “Order Type,” “Price” and “Amount” for the trade. If you would like to execute your order as soon as possible, you can click on BBO (i.e., the best bid offer).
After entering order details, you can click on [Buy (Long)] to enter a long contract (i.e., to buy BTC) or click on [Sell (Short)] if you would like to open a short position (i.e., to sell BTC).
- Buying long means that you believe the value of the asset that you are buying is going to rise over time, and you will profit from this rise with your leverage acting as a multiple on this profit. Conversely, you will lose money if the asset falls in value, again multiplied by the leverage.
- Selling short is the opposite, you believe that the value of this asset will fall over time. You will profit when the value falls, and lose money when the value increases.
For example, you can set up a limit order of 44,120 USDT and open a long position for “BTCUSDT Perp” with your desired BTC amount.
9. After placing your order, view it under [Open Orders].
Some Concepts on OKX Futures Trading
Crypto-Margined Perpetual Futures
OKX Crypto-Margined Perpetual Futures is a derivative product settled in cryptocurrencies such as BTC, with a contract size of 100USD. Traders can take a long/short position on cryptocurrencies with up to 100x leverage to make a profit when the price goes up/down.
USDT-Margined Perpetual Futures
OKX USDT-Margined Perpetual Futures is a derivative product settled in USDT. Traders can take a long/short position on cryptocurrencies with up to 100x leverage to make a profit when the price goes up/down.
Settled in crypto or USDT
OKX crypto-margined perpetual futures contracts are settled in cryptocurrencies and enable hedging and risk management by providing exposure to various crypto assets.
OKX perpetual-margined perpetual futures contracts are settled in USDT, allowing users to trade without having to hold the underlying asset.
Expiry date
Unlike traditional expiry futures contracts, perpetual futures contracts don’t have an expiry date.
Index price
USDT-margined contracts use the underlying USDT index, and crypto-margined contracts use the underlying USD index. In order to keep index prices in line with the spot market, we use prices from at least three mainstream exchanges, and adopt a special mechanism to ensure that the index price fluctuation is within the normal range when the price on a single exchange deviates significantly.
Price range
OKX adjusts the price range for each order based on the spot price and futures price at the last minute, in an effort to prevent unscrupulous investors from maliciously disrupting the market.
Mark price
In the event of extreme price fluctuations, OKX uses the mark price as reference to prevent liquidation due to a single abnormal transaction.
Tiered maintenance margin rate
The maintenance margin rate is the minimum margin rate to maintain a position. When the margin is lower than the maintenance margin + trading fee, positions will be reduced or closed. OKX adopts a tiered maintenance margin rate mechanism, i.e., for users with larger positions, the maintenance margin rate will be higher and the maximum leverage lower.
Funding rate
Since perpetual futures contracts never settle in the traditional sense, exchanges need a mechanism to ensure that futures prices and index prices converge on a regular basis. This mechanism is known as Funding Rate. The funding fee payment is made every 8 hours at 12:00 am, 8:00 am, 4:00 pm UTC. Users will only pay or receive the funding fee when they have an open position. If the position is closed prior to the funding fee settlement, no funding fees will be charged or paid.
Initial margin
Initial margin is the minimum amount of funds required to be deposited into a trading account to open a new position. This margin is used to ensure that traders can meet their obligations if the market moves against them, and it also acts as a buffer against volatile price movements. While initial margin requirements vary between exchanges, they typically represent a fraction of the total trade value. Therefore, it is crucial to manage initial margin levels carefully to avoid liquidation or margin calls. It is also advisable to keep track of the margin requirements and regulations on different platforms to optimize your trading experience.
Maintenance margin
Maintenance margin is the minimum amount of funds that an investor must maintain in their account to keep their position open. In simple terms, it is the amount of money required to hold a position in a perpetual futures contract. This is done to protect both the exchange and the investor from potential losses. If the investor fails to meet the maintenance margin, then the crypto derivatives exchange may close their position or take other actions to ensure the remaining funds are sufficient to cover the losses.
PnL
PnL stands for “profit and loss,” and it’s a way of measuring the potential gains or losses that traders can experience when buying and selling perpetual futures contracts (such as perpetual bitcoin contracts, perpetual ether contracts). Essentially, PnL is a calculation of the difference between the entry price and the exit price of a trade, taking into account any fees or funding costs associated with the contract.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is margin?
In the crypto futures market, margin is a percentage of the value of the futures contract that traders place in an account to open a position.
How is margin calculated?
OKX offers two types of margin, cross margin and isolated margin.
In Cross Margin modeThe entire margin balance is shared across open positions to avoid liquidation.
-
For crypto-margined contracts:
- Initial Margin = Contract Size*|Number of Contracts|*Multiplier / (Mark Price*Leverage)
-
For USDT-margined contracts:
- Initial Margin = Contract Size*|Number of Contracts|*Multiplier*Mark Price / Leverage
In Isolated Margin mode
Isolated Margin is the margin balance allocated to an individual position, allowing traders to manage their risk on each position.
-
For crypto-margined contracts:
- Initial Margin = Contract Size*|Number of Contracts|*Multiplier / (Average Price of Open Positions*Leverage)
-
For USDT-margined contracts:
- Initial Margin = Contract Size*|Number of Contracts|*Multiplier*Average Price of Open Positions / Leverage
What are the difference between Margin andLeverage?
Leverage is a type of trading mechanism that investors use to trade with more capital than they currently own. It amplifies potential returns and the risk they take.
In Cross Margin mode, when the user opens a certain number of long or short positions, Initial Margin = Position Value / Leverage
Crypto-margined contracts
- e.g. If the current BTC price is $10,000, the user wants to buy perpetual contracts worth 1 BTC with 10x leverage, the Number of Contracts = BTC Quantity*BTC Price / Contract Size = 1*10,000/100 = 100 contracts.
- Initial Margin = Contract Size*Number of Contracts / (BTC Price*Leverage) = 100*100 / ($10,000*10) = 0.1 BTC
USDT-margined contracts
- e.g. If the current BTC price is $10,000 USDT/BTC, the user wants to buy perpetual contracts worth 1 BTC with 10x leverage, the Number of Contracts = BTC Quantity / Contract Size = 1/0.01 = 100 contracts.
- Initial Margin = Contract Size*Number of Contracts*BTC Price / Leverage) = 0.01*100*10,000 / 10=1,000 USDT
How to calculate Margin rate
- Initial Margin: 1/Leverage
- Maintenance Margin: The minimum margin rate required for the user to maintain the current position.
-
Single-currency cross margin:
- Initial Margin = (Currency Balance + Earnings -Trading Volume of Pending Maker Sell Orders in the Selected Currency - Trading Volume of Pending Maker Buy Options Orders in the Selected Currency - Trading Volume of Pending Isolated Margin Positions in the Selected Currency - Trading Fees of All Maker Orders) / (Maintenance Margin + Liquidation Fee).
-
Multi-currency cross margin:
- Initial Margin = Adjusted Equity / (Maintenance Margin + Trading Fee)
-
Single- and multi-currency isolated margin / Portfolio margin:
- Crypto-margined contracts: Initial Margin = (Margin Balance + Earnings) / (Contract Size * |Number of Contracts| / Mark Price*(Maintenance Margin + Trading Fee))
- USDT-margined contracts: Initial Margin = (Margin Balance + Earnings) / (Contract Size * |Number of Contracts| * Mark Price*(Maintenance Margin + Trading Fee))
What are Margin calls?
In Isolated Margin mode, users can increase the margin for a specific position for better risk control.
What is Leverage adjustment?
OKX allows users to adjust the leverage for open positions. If the adjusted leverage is less than the maximum leverage of the current position, the user can increase the leverage, while the initial margin will be reduced. Conversely, when the user reduces the leverage, the initial margin will increase if there is available balance in the account.